Understanding the Establishment-based Risk Assessment model for Hatcheries
The Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) is strongly committed to its mission to safeguard food, animals and plants to enhance the health and well-being of Canada's people, environment and economy.
Risks to food safety and our animal and plant resources have changed considerably in recent years and will continue to evolve rapidly with global trading patterns, innovation and new technologies. In this fast-paced environment, the CFIA must continue to become more agile to help protect our resources while also supporting industry's ability to compete globally.
As part of the Agency's efforts to modernize its inspection system, the Establishment-based Risk Assessment model for Hatcheries (ERA-H) was developed to evaluate the food safety risk (Salmonella spp.) that the food products (poultry meat, eggs, balut) derived from Canadian hatcheries may represent to the consumers. The model uses data and a mathematical algorithm to determine the level of risk to inform oversight required by inspectors.
The CFIA worked together with academia, industry and government partners to create this tool to provide a consistent and efficient approach to inspection.
How the Establishment-based Risk Assessment model for hatcheries works
The ERA-H model identifies areas of higher risk and indicates where inspectors should be spending more time.
Using scientific data, hatchery-specific information gathered from regulated parties and the compliance history of a hatchery, the ERA-H model evaluates a hatchery based on three different groups of risk factors and determines their level of risk (see image below).
This means that higher risk hatcheries that require urgent attention can be easily identified and focused on.
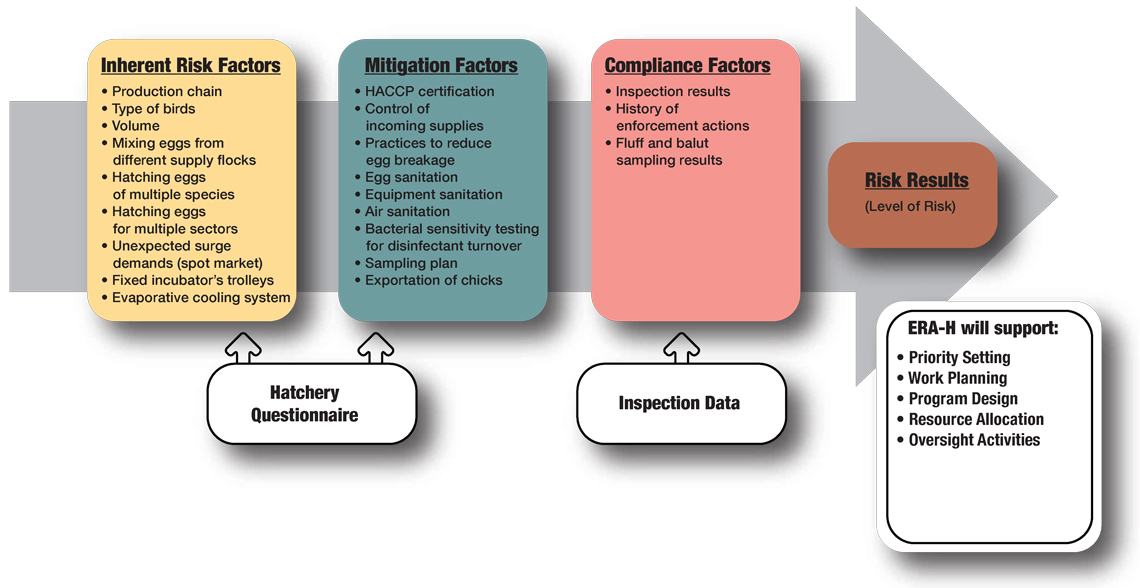
Description for image – ERA-H model arrow illustration
This figure illustrates the model design as an arrow. The ERA-H model has three clusters: inherent risk factors, the mitigation factors, and the compliance factors represented by the first, second and third boxes, respectively. Each box presents the list of risk factors. The first two clusters are collected through a questionnaire provided to regulated parties and the last cluster is collected through inspection data. This then generates the final risk results (level of risk) that will support priority setting, work planning, program design, resource allocation and oversight activities.
The Implementation of the Establishment-based Risk Assessment model for hatcheries in federally regulated hatcheries
Implementation of the ERA-H model is impacting the frequency of CFIA oversight. Hatcheries are able to access their individual results and work with the CFIA on strategies to mitigate potential areas of concern.
The model is flexible to adapt to emerging and scientific trends in food safety and innovative practices that may be implemented at a hatchery.

Description for image – How the ERA-H model assigns hatcheries a food safety risk level
This figure depicts a graph with three bars representing the risk level from the ERA-H model from low to high risk on the vertical axis. The first bar represents the risk level when considering the inherent risk factors such as the type of birds and the volume. The second bar represents the risk level when considering the inherent risk factors combined with the mitigation factors such as HACCP certification. The last bar represents the final risk considering the inherent risk factors, mitigation factors and compliance factors. Compliance factors include information about how well the hatchery has been complying with regulatory requirements.
Industry involvement in the Establishment-based Risk Assessment model for hatcheries
Hatcheries are invited to provide information about their mitigation measures and operational activities through a questionnaire provided by the ERA-H team. This information along with the compliance assessment of hatcheries are being used to populate the ERA-H model and produce risk profiles for each hatchery. Results from the ERA-H model are actually integrated in the Agency's work planning.
Updates to the Establishment-based Risk Assessment model for hatcheries
The CFIA will review and update the ERA-H model on an ongoing basis, using the most up-to-date science, technology, and risk assessment approaches. It is designed to adapt quickly to emerging global and scientific trends, new risks and changes within hatcheries.
For questions or comments, email: cfia.eramodel-modeleere.acia@inspection.gc.ca.
Resources
- Date modified:
- Date modified:
