Using Control Zones to Manage Animal Disease Risk
A control zone is a defined area that is established to prevent the spread of animal disease from an infected area to areas free of the disease. Movement restrictions may be placed on certain products leaving, going into, or moving within the control zone.
Zoning is an internationally recognized practice to manage disease risk and maintain trade. It is one tool within a suite of measures that the CFIA uses to respond to animal diseases in Canada. A typical zoning strategy would include:
- a primary control zone where the disease has been detected, or is suspected to exist; and
- a secondary control zone where the disease is not suspected to exist and is a buffer between the primary control zone and the rest of Canada.
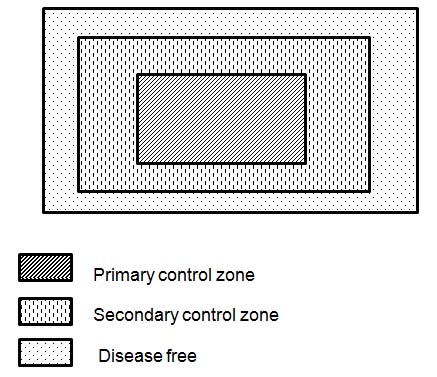
Description of image - Control Zones
The image illustrates one way how the CFIA can establish primary and secondary control zones to respond to animal disease in Canada, and prevent disease from spreading to unaffected areas. In this illustration, a primary control zone resides within a larger secondary control zone. This secondary control zone acts as a buffer from the rest of Canada and resides within a larger area that is free of disease.
The CFIA determines if zones are required based on the unique circumstances of each disease situation. Some factors included in this determination are the nature of the disease, presence of the disease in wildlife or the environment, potential for disease spread and geographical features in the area (i.e., waterways, roads, terrain).
When a foreign animal disease is first detected, the goal of the zone is to rapidly contain and eradicate the disease. If the disease can be eradicated from an animal population, then the size of the zone could be slowly reduced or targeted until the disease is gone and the zone is no longer necessary.
If a disease becomes established in a geographic area and cannot be eradicated, then the zone could remain in place for a long time or be enlarged. This often applies when a disease has become endemic in the local wildlife populations because it is more difficult to implement effective controls on wildlife.
As described in the following tables, the CFIA can implement a variety of disease measures based on the specific details of each disease investigation.
| Primary Control Zone | Established disease | Foreign disease |
|---|---|---|
| Movement controls - leaving the zone | Yes | Yes |
| Movement controls - within the zone | Yes, but minimal | Yes, very strict |
| Movement controls - into the zone | Yes, but minimal | Yes, very strict |
| Disease controls (depopulation, cleaning and disinfection) within the zone | Minimal or none | Yes, aggressive response |
| Disease surveillance | No | Yes |
| Geographic area of zone | May enlarge over time if the disease spreads to new areas | Goal is to reduce size and eliminate |
| Secondary Control Zone | Established disease | Foreign disease |
|---|---|---|
| Movement controls - leaving the zone | No | No |
| Movement controls - within the zone | No | No |
| Movement controls – into the zone | No | No |
| Disease controls for new cases | Yes, aggressive response | Yes, aggressive response |
| Surveillance | Yes | Yes |
| Geographic area of zone | May enlarge over time | Goal is to reduce size and eliminate |
For more information:
- Date modified: